Note
Click here to download the full example code
Single Gramian angular field¶
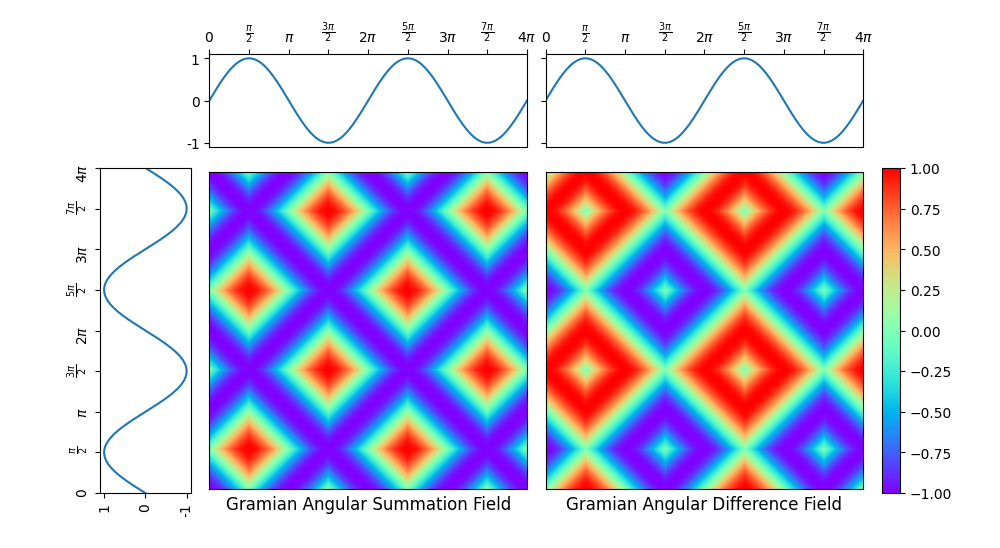
A Gramian angular field is an image obtained from a time series, representing
some kind of temporal correlation between each pair of values from the time
series. Two methods are available: Gramian angular summation field and Gramian
angular difference field.
It is implemented as pyts.image.GramianAngularField.
In this example, the considered time series is the sequence of the sine
function values for 1000 equally-spaced points in the interval
.
Both the corresponding Gramnian angular summation and difference fields are
plotted.
Since the API is designed for machine learning, the
transform() method of the
pyts.image.GramianAngularField class expects a data set of time series
as input, so the time series is transformed into a data set with a single time
series (X = np.array([x])) and the first element of the data set of
Gramian angular fields is retrieved (ax_gasf.imshow(X_gasf[0], ...).
# Author: Johann Faouzi <johann.faouzi@gmail.com>
# License: BSD-3-Clause
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pyts.image import GramianAngularField
# Create a toy time series using the sine function
time_points = np.linspace(0, 4 * np.pi, 1000)
x = np.sin(time_points)
X = np.array([x])
# Compute Gramian angular fields
gasf = GramianAngularField(method='summation')
X_gasf = gasf.fit_transform(X)
gadf = GramianAngularField(method='difference')
X_gadf = gadf.fit_transform(X)
# Plot the time series and its recurrence plot
width_ratios = (2, 7, 7, 0.4)
height_ratios = (2, 7)
width = 10
height = width * sum(height_ratios) / sum(width_ratios)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(width, height))
gs = fig.add_gridspec(2, 4, width_ratios=width_ratios,
height_ratios=height_ratios,
left=0.1, right=0.9, bottom=0.1, top=0.9,
wspace=0.1, hspace=0.1)
# Define the ticks and their labels for both axes
time_ticks = np.linspace(0, 4 * np.pi, 9)
time_ticklabels = [r'$0$', r'$\frac{\pi}{2}$', r'$\pi$',
r'$\frac{3\pi}{2}$', r'$2\pi$', r'$\frac{5\pi}{2}$',
r'$3\pi$', r'$\frac{7\pi}{2}$', r'$4\pi$']
value_ticks = [-1, 0, 1]
reversed_value_ticks = value_ticks[::-1]
# Plot the time series on the left with inverted axes
ax_left = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 0])
ax_left.plot(x, time_points)
ax_left.set_xticks(reversed_value_ticks)
ax_left.set_xticklabels(reversed_value_ticks, rotation=90)
ax_left.set_yticks(time_ticks)
ax_left.set_yticklabels(time_ticklabels, rotation=90)
ax_left.set_ylim((0, 4 * np.pi))
ax_left.invert_xaxis()
# Plot the time series on the top
ax_top1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 1])
ax_top2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0, 2])
for ax in (ax_top1, ax_top2):
ax.plot(time_points, x)
ax.set_xticks(time_ticks)
ax.set_xticklabels(time_ticklabels)
ax.set_yticks(value_ticks)
ax.xaxis.tick_top()
ax.set_xlim((0, 4 * np.pi))
ax_top1.set_yticklabels(value_ticks)
ax_top2.set_yticklabels([])
# Plot the Gramian angular fields on the bottom right
ax_gasf = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 1])
ax_gasf.imshow(X_gasf[0], cmap='rainbow', origin='lower',
extent=[0, 4 * np.pi, 0, 4 * np.pi])
ax_gasf.set_xticks([])
ax_gasf.set_yticks([])
ax_gasf.set_title('Gramian Angular Summation Field', y=-0.09)
ax_gadf = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 2])
im = ax_gadf.imshow(X_gadf[0], cmap='rainbow', origin='lower',
extent=[0, 4 * np.pi, 0, 4 * np.pi])
ax_gadf.set_xticks([])
ax_gadf.set_yticks([])
ax_gadf.set_title('Gramian Angular Difference Field', y=-0.09)
# Add colorbar
ax_cbar = fig.add_subplot(gs[1, 3])
fig.colorbar(im, cax=ax_cbar)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.560 seconds)

