Note
Click here to download the full example code
Symbolic Aggregate approXimation¶
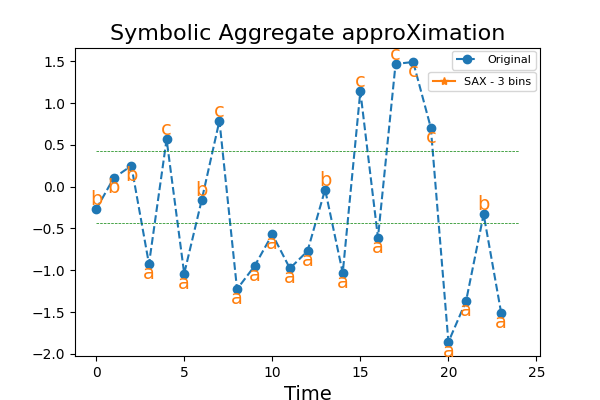
Binning continuous data into intervals can be seen as an approximation that
reduces noise and captures the trend of a time series. The Symbolic Aggregate
approXimation (SAX) algorithm bins continuous time series into intervals,
transforming independently each time series (a sequence of floats) into a
sequence of symbols, usually letters. This example illustrates the
transformation.
It is implemented as
pyts.approximation.SymbolicAggregateApproximation.
# Author: Johann Faouzi <johann.faouzi@gmail.com>
# License: BSD-3-Clause
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.lines as mlines
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import norm
from pyts.approximation import SymbolicAggregateApproximation
# Parameters
n_samples, n_timestamps = 100, 24
# Toy dataset
rng = np.random.RandomState(41)
X = rng.randn(n_samples, n_timestamps)
# SAX transformation
n_bins = 3
sax = SymbolicAggregateApproximation(n_bins=n_bins, strategy='normal')
X_sax = sax.fit_transform(X)
# Compute gaussian bins
bins = norm.ppf(np.linspace(0, 1, n_bins + 1)[1:-1])
# Show the results for the first time series
bottom_bool = np.r_[True, X_sax[0, 1:] > X_sax[0, :-1]]
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
plt.plot(X[0], 'o--', label='Original')
for x, y, s, bottom in zip(range(n_timestamps), X[0], X_sax[0], bottom_bool):
va = 'bottom' if bottom else 'top'
plt.text(x, y, s, ha='center', va=va, fontsize=14, color='#ff7f0e')
plt.hlines(bins, 0, n_timestamps, color='g', linestyles='--', linewidth=0.5)
sax_legend = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='#ff7f0e', marker='*',
label='SAX - {0} bins'.format(n_bins))
first_legend = plt.legend(handles=[sax_legend], fontsize=8, loc=(0.76, 0.86))
ax = plt.gca().add_artist(first_legend)
plt.legend(loc=(0.81, 0.93), fontsize=8)
plt.xlabel('Time', fontsize=14)
plt.title('Symbolic Aggregate approXimation', fontsize=16)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.700 seconds)

