Note
Click here to download the full example code
Word ExtrAction for time SEries cLassification (WEASEL)¶
Bag-of-words approaches are common in time series classification. The
Word ExtrAction for time SEries cLassification (WEASEL) algorithm extracts
words from time series and builds features representing frequencies of each
word for each time series.
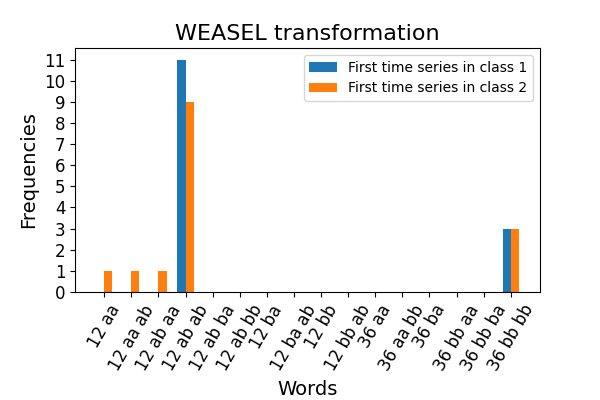
This example illustrates the words and the frequencies of these words that
have been learned by this algorithm.
It is implemented as pyts.transformation.WEASEL.
# Author: Johann Faouzi <johann.faouzi@gmail.com>
# License: BSD-3-Clause
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pyts.datasets import load_gunpoint
from pyts.transformation import WEASEL
# Toy dataset
X_train, _, y_train, _ = load_gunpoint(return_X_y=True)
# WEASEL transformation
weasel = WEASEL(word_size=2, n_bins=2, window_sizes=[12, 36], sparse=False)
X_weasel = weasel.fit_transform(X_train, y_train)
# Visualize the transformation for the first time series
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
vocabulary_length = len(weasel.vocabulary_)
width = 0.3
plt.bar(np.arange(vocabulary_length) - width / 2, X_weasel[y_train == 1][0],
width=width, label='First time series in class 1')
plt.bar(np.arange(vocabulary_length) + width / 2, X_weasel[y_train == 2][0],
width=width, label='First time series in class 2')
plt.xticks(np.arange(vocabulary_length),
np.vectorize(weasel.vocabulary_.get)(np.arange(X_weasel[0].size)),
fontsize=12, rotation=60)
y_max = np.max(np.concatenate([X_weasel[y_train == 1][0],
X_weasel[y_train == 2][0]]))
plt.yticks(np.arange(y_max + 1), fontsize=12)
plt.xlabel("Words", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("Frequencies", fontsize=14)
plt.title("WEASEL transformation", fontsize=16)
plt.legend(loc='best', fontsize=10)
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.27)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.211 seconds)

