Note
Click here to download the full example code
Shapelet Transform¶
The Shapelet Transform algorithm extracts shapelets from a data set of
time series and returns the distances between the shapelets and the time
series. A shapelet is defined as a subset of a time series, that is a
set of values from consecutive time points. The distance between a shapelet
and a time series is defined as the minimum of the distances between this
shapelet and all the shapelets of same length extracted from this time series.
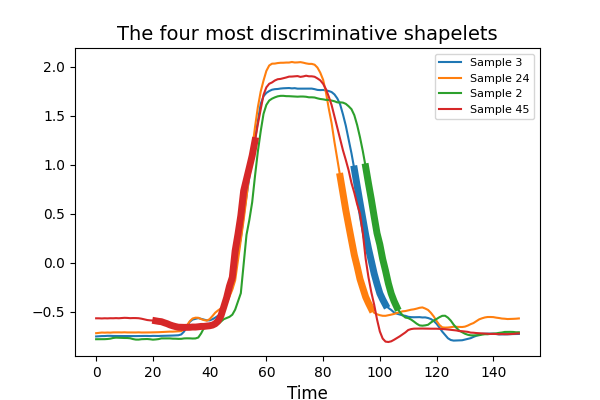
The most discriminative shapelets are selected.
This example illustrates the transformation of this algorithm and highlights
the most discriminative shapelets that have been selected. It is implemented
as pyts.transformation.ShapeletTransform.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pyts.datasets import load_gunpoint
from pyts.transformation import ShapeletTransform
# Toy dataset
X_train, _, y_train, _ = load_gunpoint(return_X_y=True)
# Shapelet transformation
st = ShapeletTransform(window_sizes=[12, 24, 36, 48],
random_state=42, sort=True)
X_new = st.fit_transform(X_train, y_train)
# Visualize the four most discriminative shapelets
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
for i, index in enumerate(st.indices_[:4]):
idx, start, end = index
plt.plot(X_train[idx], color='C{}'.format(i),
label='Sample {}'.format(idx))
plt.plot(np.arange(start, end), X_train[idx, start:end],
lw=5, color='C{}'.format(i))
plt.xlabel('Time', fontsize=12)
plt.title('The four most discriminative shapelets', fontsize=14)
plt.legend(loc='best', fontsize=8)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 1 minutes 7.010 seconds)

